Understanding Propane Vented Heaters: A Comprehensive Guide


Intro
Understanding heating solutions is crucial for anyone involved in agriculture, horticulture, or simply looking for effective means to maintain warmth in larger spaces. Among various heating options available, propane vented heaters stand out due to their efficiency and versatility. They are designed to operate in various settings, providing a reliable source of heat, especially in areas where electricity might be less dependable. This guide aims to unravel the layers of propane vented heaters, providing insights into their design, functionality, and applications, thus equipping readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions in their heating choices.
Key Concepts and Terminology
Basic Definitions
Before diving deep into heating solutions, it’s important to grasp what propane vented heaters are. In layman's terms, these heaters burn propane gas to produce heat, which is then emitted into the surrounding environment via ventilation systems. Unlike ventless heaters, propane vented heaters expel combustion gases outside, making them a safer option for enclosed spaces.
Historical Context
Historically, propane was utilized as a fuel source during World War II, but its efficiency as a heating medium became recognized shortly thereafter. In agricultural realms, the adoption of propane vented heaters has gained momentum as more farmers seek effective and economical solutions for protecting crops from cold weather. Over time, innovations in design have ensured these heaters not only meet safety standards but also operate more efficiently, catering to the growing needs of modern agriculture.
Recent Innovations and Trends
Technological Advancements
The breakthrough in heater technology has significantly enhanced propane vented heaters. Today's models feature advanced thermostatic controls, ensuring optimal temperature regulation. Digital displays provide instant feedback, while some can even integrate with smart home systems for remote management. Moreover, improvements in insulation and materials have made them more durable and efficient compared to their predecessors.
Sustainable Practices
As the farming world increasingly moves toward sustainability, many manufacturers of propane vented heaters are adopting greener practices. Utilizing more environmentally friendly materials, along with incorporating features that optimize fuel consumption, are becoming standard. This focus on sustainability not only caters to conscientious consumers but also aligns with broader agricultural practices that emphasize environmental stewardship.
Practical Applications and Techniques
Step-by-step Guides
When it comes to installation, following a systematic approach makes all the difference. Here’s a simplified outline for installing a propane vented heater:
- Choose the right location: Ensure the heater is placed in a strategic location for optimal heat distribution, preferably away from flammable materials.
- Secure ventilation: Ensure proper venting outside to dispose of any combustion gases efficiently.
- Connect the propane supply: Use appropriate fittings and ensure all connections are secure and leak-free.
- Test the heater: Before finalizing the setup, conduct a test to ensure it operates smoothly.
Case Studies
A practical example of propane vented heaters in action can be seen in the expansion of pumpkin farms in regions with unpredictable weather patterns. Farmers utilizing these heaters have reported significant improvements in crop yield due to better temperature control, allowing for extended growing seasons. Moreover, such heaters have been vital in protecting delicate seedlings from frost, demonstrating their critical role in agricultural success.
"The shift to propane vented heaters has transformed our operation, allowing us to optimize not just heating but overall resource management," says a local farmer who adopted this technology last season.
In summary, propane vented heaters are not just another heating option; they represent a significant advancement in how agricultural heating is approached. Understanding their design, functionality, and advantages provides farmers with essential tools to enhance their productivity and ensure the stability of their ventures. For further reading about propane technology, you may check out Wikipedia or agricultural education resources such as Britannica.
Prologue to Propane Vented Heaters
In the ever-evolving landscape of agricultural practices, keeping crops and livestock in optimal conditions is paramount. Propane vented heaters emerge as a reliable option for farmers and agricultural professionals. These heaters not only provide uniform warmth but also enhance productivity by creating environments where plants and animals can thrive, even during the coldest months.
Definition and Purpose
So, what exactly is a propane vented heater? In simple terms, it's a heating device powered by propane gas that expels combustion gases outside through a venting system. The primary purpose of these heaters is to transfer heat efficiently into a designated space, often where plants are grown or where animals are sheltered. This process prioritizes safety while ensuring that ventilation is adequate to prevent harmful gas buildup.
Farmers widely appreciate the efficacy of propane vented heaters due to their ability to deliver substantial heat quickly. Unlike electric heaters, which may take time to heat a space, propane options can reach set temperatures almost instantly. This responsiveness is particularly advantageous in agricultural settings where climate control is crucial for maintaining crop quality and animal welfare.
Historical Context
The use of gas as a source of heating dates back centuries but has seen significant advancements in the last few decades. Interestingly, propane fuel itself was discovered in 1910 but gained traction only after World War II when economic conditions allowed farmers the means to adopt these innovations.
In the mid-20th century, many agricultural operations began transitioning from traditional wood or coal-fired heating solutions to more efficient propane systems. As technology has progressed, current propane vented heaters have evolved to include enhanced safety features and improved efficiency. They minimize waste while maximizing output, which is a critical consideration in an era where every penny counts in farming operations.
Furthermore, the rise of environmental awareness has pushed more farmers to seek heating solutions that are both effective and sustainable. Propane vented heaters fit this mold well, as they produce fewer emissions compared to some other heating methods, making them a favorable option a longside their historical relevance in agriculture.
Propane vented heaters have a rich legacy in agriculture, evolving remarkably from basic heat sources to essential tools that maximize efficiency and minimize environmental impact.
As the agricultural sector becomes increasingly conscious of heating solutions' efficacy and environmental effects, understanding the nuances of propane vented heaters allows professionals to adopt practices that benefit both their operations and the planet.
Design and Mechanism
Understanding the design and mechanism of propane vented heaters is crucial for those who rely on them, especially in agricultural settings. These heaters are not just simple devices; they represent a blend of engineering and practical necessity. Their design features directly influence efficiency, ease of use, and safety—a trifecta of importance when considering heating solutions in environments like greenhouses, animal housing, or crop processing.
Components of Propane Vented Heaters
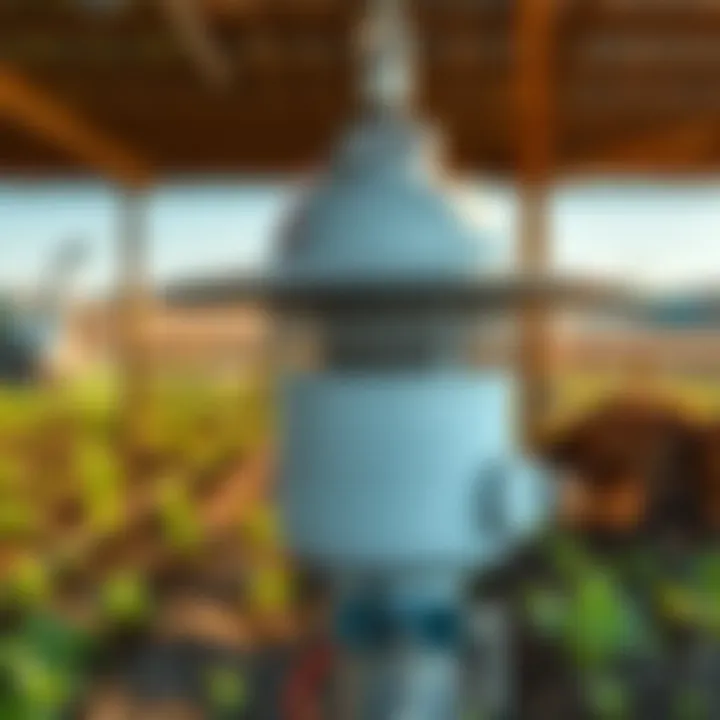


Each component of a propane vented heater serves a vital role in its operation, ensuring that it functions optimally and safely.
Burner Assembly
The burner assembly is the heart of a propane vented heater. Its primary function is to ignite propane gas and convert it into heat through combustion. A key characteristic of this assembly is the efficiency with which it burns fuel. Many modern units incorporate technology that enhances combustion efficiency, leading to reduced emissions and lower fuel costs. This is critical for farmers looking to save on operational expenses.
A unique feature of the burner assembly is its modulating capability, allowing for adjustments based on the specific heating needs at any given time. This variability is beneficial because it minimizes energy waste. However, it can also make the initial setup slightly complex as it requires careful calibration.
Heat Exchanger
Moving on, the heat exchanger is integral to transferring heat from the burning gases to the air circulated within the space. This component stands out due to its material composition, often made from durable steel or aluminum, which supports high thermal conductivity. This characteristic makes the heat exchanger effective in quickly warming the space while ensuring longevity against wear from constant heating cycles.
One distinct advantage is the design configuration, often being finned or tubular, which increases surface area and promotes better heat transfer. That said, the downside can be the cleanliness factor. Over time, particulates and soot can build up, requiring regular maintenance to keep it functioning efficiently.
Ventilation System
Lastly, the ventilation system plays a crucial role in safely expelling exhaust gases produced during combustion. A primary element of this system is the ability to ensure proper air flow to maintain safe operation. It typically includes a series of ducts and flues designed to direct harmful gases outside, which is especially important in enclosed spaces like greenhouses.
The key characteristic of modern ventilation systems is their safety mechanisms, which may include pressure relief vents to prevent backdrafts. This attention to safety is paramount for users who prioritize risk mitigation when employing heaters in their business.
A unique feature here is the ability for some systems to integrate with home automation systems, providing real-time monitoring and control over the environment. However, the complexity of installation can be a downside, especially for users who may not have technical expertise.
How it Works
Now, let’s unravel how these components work in harmony.
Propane vented heaters operate by pulling propane gas from a tank, which is then directed to the burner assembly where it is ignited. The heat from the burning gas is then transferred to the heat exchanger, heating the surrounding air.
Once heated, the air is circulated back into the space needing warmth. The exhaust created during this process is expelled through the ventilation system, maintaining a safe and healthy environment. This full cycle of operation is why it’s crucial to ensure all components are functioning properly.
When all is said and done, understanding the design and mechanism of these heaters sheds light on the sophistication involved in what might seem like a simple tool. By knowing how each component interacts, users are better equipped to make informed decisions regarding their heating needs.
Applications in Agricultural Settings
In the realm of agriculture, maintaining an optimal climate can spell the difference between a bountiful harvest and a disappointing yield. Enter propane vented heaters. These devices are not merely a luxury; they are often a necessity in various agricultural scenarios. Here, we examine their critical roles for heating greenhouses, ensuring animal comfort, and facilitating effective crop drying and processing.
Heating Greenhouses
Greenhouses provide a controlled environment for plant growth. However, the weather outside can often be unpredictable, and that’s where propane vented heaters come into play. By using these heaters, farmers can achieve a consistent temperature within their greenhouses, protecting delicate plants from frost damage during colder months.
The heaters efficiently distribute warm air and create a stable environment. This also means higher crop yields and improved quality. Imagine a greenhouse filled with young tomato plants needing just the right amount of warmth. Propane vented heaters ensure those seedlings are not left shivering while waiting for the sun to come out.
Some noteworthy aspects of greenhouse heating include:
- Temperature Regulation: Maintaining the ideal temperature can boost growth rates significantly.
- Uniform Heat Distribution: Unlike traditional heaters that might leave cold spots, propane heaters circulate warmth evenly.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While initial setup may seem steep, the long-term savings on energy bills often offset the investment.
"Controlled environments lead to refined and robust crops, which are the backbone of any successful farm."
Animal Housing
Livestock comfort is paramount. Propane vented heaters play a crucial role in barns and animal shelters by maintaining a comfortable temperature for cows, pigs, and chickens. When temperatures drop, animals can suffer from stress, which ultimately affects their health and productivity. The right heating system can keep animals content and safe from hypothermia.
Moreover, these heaters are particularly useful in calf nurseries, where newborns are highly susceptible to cold. A stable, warm environment helps bolster their immune systems and ensures proper growth. Some points to consider include:
- Health Benefits for Animals: Warmer surroundings reduce stress and illness among livestock.
- Ventilation Matters: Ensuring proper ventilation alongside heating prevents moisture buildup, which can lead to diseases.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern propane heaters are designed to consume less fuel while delivering consistent heat, allowing for more sustainable farming practices.
Crop Drying and Processing
After harvest, the next significant challenge is to dry and process crops effectively. Propane vented heaters provide an efficient solution to this issue, promoting quicker drying times and reducing the risk of mould and spoilage.
Whether it's drying grains, fruits, or herbs, these heaters manage moisture levels to ensure that products are safely stored without losing quality. Efficient drying can also lead to improved market price, as fresh, dry crops command better rates. Key considerations include:
- Reduced Spoilage: Quick drying helps preserve quality and value.
- Versatility: From grains to herbs, propane heaters can be adapted for different drying processes.
- Cost Savings: Faster drying times translate to less energy consumed overall, reinforcing the case for choosing propane vented systems.
Benefits of Using Propane Vented Heaters
Propane vented heaters have carved out a significant niche in the agricultural sector, and for good reason. They not only provide warmth but also ensure efficiency and sustainability. When comparing heating alternatives, it’s essential to understand how propane vented heaters stack up in terms of operational costs, energy efficiency, and environmental responsibility. This section aims to shine a light on these key benefits, offering insights tailored for farmers and agricultural enthusiasts.
Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness

The efficiency of propane vented heaters cannot be overstated; they stand out as a reliable source of heat that maximizes energy usage. For instance, many models boast efficiencies exceeding 90%. This means that very little energy is wasted, translating to lower utility bills for users.
To break it down further:
- High Heat Output: Propane produces more heat per unit compared to other fuels, making it an effective choice for heating spaces quickly.
- Lower Operation Costs: With competitive prices and efficient models, the long-term savings add up. Farmers who regularly monitor their fuel expenses can find that using propane heaters can yield noticeable reductions in heating costs during colder months.
"Choosing the right heater is like picking the right tool. It not only saves you money but also keeps your operations efficient."
Moreover, considering current trends, propane's availability and pricing relative to electric and oil heating options make it a smart choice, especially in rural areas where electric service may be limited or electricity prices can soar.
Sustainability Considerations
In an era where sustainability is front and center, propane vented heaters offer a cleaner burning alternative to traditional fossil fuels. Propane produces significantly lower emissions, particularly when compared to heating oil or traditional electric systems that may draw from coal-powered grids.
When looking at sustainability:
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Because propane burns efficiently, its carbon emissions are considerably less. This aligns well with the growing desire among consumers and farmers alike to reduce their environmental impact.
- Renewable Potential: Another key point to consider is the potential for renewable propane. Some companies are investing in creating propane from renewable sources, which can further enhance the sustainability of this heating option.
In practical terms, adopting propane vented heaters can contribute to greener practices in agriculture, an important consideration for many modern farmers who are conscious of their ecological footprint.
Installation and Maintenance
The installation and maintenance of propane vented heaters play a pivotal role in ensuring their efficiency, safety, and longevity. Understanding these processes not only empowers agricultural professionals to optimize their heating solutions but also promotes a safe environment for plants and livestock. Poor installation can result in significant problems down the line, whereas regular maintenance can prevent minor issues from escalating into costly repairs or safety hazards. This is especially important in agricultural settings where climate control directly impacts productivity and sustainability.
Installation Process
The installation process for a propane vented heater includes several key steps that require attention to detail. Here’s a breakdown to guide those looking to set up such systems:
- Choosing the Right Location: Select a site that allows proper clearance from combustible materials and ensures adequate venting. The heater should be positioned to allow warm air to circulate effectively.
- Preparing the Ventilation Path: Determine the venting route. This should be free of obstructions and follow local building codes and regulations. Using approved materials for venting is critical for safety.
- Connecting the Heater to the Gas Supply: Ensure that there is a secure connection to the propane tank. All connections should be tight to prevent leaks. Sealing compounds specifically designed for gas applications should be utilized.
- Mounting the Heater: Depending on the model, some heaters may need to be hung or mounted to walls or ceilings. Make sure it is secured adequately and is level to operate efficiently.
- Testing for Leaks: After installation, it is essential to check for gas leaks by using a solution of soap and water. Bubbles will form at the site of a leak, signaling the need for repairs. Always double-check the entire installation before firing up the heater.
- Following Manufacturer's Instructions: Every unit will come with specific guidelines. Adhering to these ensures proper operation and compliance with safety standards.
By paying attention to these steps, farmers and agricultural enthusiasts can set up their propane vented heaters effectively, reducing the risk associated with improper installation.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
Routine maintenance tasks are vital for keeping propane vented heaters running efficiently. Neglecting these can lead to reduced performance or unsafe conditions. Consider these essential maintenance practices:
- Regular Inspections: Schedule annual inspections to check for corrosion, wear, or other issues. It's best to engage a professional who can assess the overall condition.
- Cleaning the Burner: Dust and debris can accumulate in the burner assembly. Cleaning it ensures that the heater can operate smoothly without interruptions.
- Examining the Vent System: Over time, vent systems can become obstructed. Clear any blockages, ensuring that gases can escape freely.
- Checking the Gas Connections: Look for any signs of wear or damage in the gas lines and fittings. Tighten connections as necessary, and replace any faulty sections promptly.
- Changing Filters: Some heaters come with air filters that need replacement or cleaning. Regularly changing filters helps in maintaining efficiency.
Employing these routine maintenance tasks not only enhances the lifespan of propane heaters but also safeguards the environment in which they operate.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When using propane vented heaters, various issues may arise. Understanding common problems and their remedies can save time, resources, and frustration. Here are some of the more frequent challenges:
Inconsistent Heat Output: If the heater is not providing consistent warmth, check the thermostat settings and ensure that there is a good flow of air. Sometimes, adjusting the thermostat or cleaning elements can resolve the issue.
Odor of Gas: A strong smell may indicate a gas leak. It's crucial to evacuate the space immediately and contact a professional service to assess and fix the issue. Never ignore this warning signal.
Pilot Light Issues: If the pilot light keeps going out, it could indicate a draft or a faulty thermocouple. Checking for possible drafts in the area is a good start, followed by an examination of the thermocouple.
Noise During Operation: Unusual noises can arise if there are loose components or a malfunctioning blower. Inspecting for loose screws and tightening them may alleviate the problem.
Overheating: An overheating unit may be a signal of blocked vents or the need for a maintenance check. Addressing these concerns is essential for safe operation.
In a nutshell, prompt identification and resolution of these issues not only ensure functional heaters but also avoid larger problems in the future that could disrupt agricultural processes.
"Routine check-ups and preventive measures can save both time and money, allowing you to focus on what matters most: fostering a thriving agricultural business."
Safety Considerations
Understanding safety precautions related to propane vented heaters is essential, especially in agricultural settings where these heating solutions are often deployed. Ensuring the safety of both the operators and the surrounding environment is paramount. Neglecting safety can lead to dire consequences, including potential injuries or property damage due to gas leaks or inadequate ventilation. By focusing on safety training and establishing thorough protocols, one can enhance the efficiency of heating systems while minimizing risks associated with propane use.
Gas Leak Precautions
Gas leaks are a serious concern when using propane vented heaters. A small leak can result in significant hazards, including fire risks and health issues due to inhalation. Therefore, taking preventive measures is crucial.
- Regular Inspection: Regularly inspect the heater and connection points for signs of wear or damage. Look for any cracks or corrosion that may develop over time.
- Gas Detectors: Invest in propane gas detectors. These devices can alert you to a leak before it becomes a serious problem. Ensure they are placed in areas where propane is used or stored.
- Immediate Action: If a gas smell is detected, turn off all appliances and do not use electrical switches. Evacuate the space and contact a professional to address the leak. Always prioritize safety first.
- Safe Storage: Store propane tanks outdoors in a well-ventilated space away from any ignition sources. This minimizes the risk of leakage and potential fires.
"Prevention is always better than cure. In the case of propane, it's about protecting lives and property."


Ventilation Requirements
Ventilation is a crucial aspect when utilizing propane vented heaters. Proper ventilation ensures that any combustion gases are safely expelled, providing a healthier environment.
- Adequate Airflow: Ensure that your space has adequate airflow to maintain safe levels of oxygen. Poor ventilation can cause toxic gases to accumulate, posing serious health risks.
- Chimney or Flue Installation: It’s essential to install a proper chimney or flue system that complies with local regulations. These systems should effectively channel exhaust gases outside, away from the heating area.
- Air Entry Points: Ensure there are sufficient entry points for fresh air. This includes opening windows or employing vent fans when necessary, especially in enclosed spaces.
- Compliance: Adhere to local and national guidelines regarding ventilation as these laws are put in place to protect users from hazards associated with poor gas management.
Comparative Analysis
Understanding how propane vented heaters stack up against other heating technologies is critical for making informed decisions in agricultural practices. A comparative analysis highlights the strengths and weaknesses of propane heaters, providing essential insights into their operational efficiency, cost implications, and suitability for various agricultural settings. The ability to juxtapose propane with other heating options like electric and oil heaters allows farmers and enthusiasts to pinpoint the best choice for their unique requirements.
Propane vs. Electric Heaters
When it comes to selecting an appropriate heating system, the comparison between propane and electric heaters often takes center stage. Here are some important factors to consider:
- Energy Source: Propane is a fossil fuel, while electric heaters depend on electricity, which may come from renewable or non-renewable sources. This distinction has implications for sustainability and carbon footprint.
- Cost Efficiency: In terms of operation, propane heaters generally exhibit greater cost efficiency particularly in regions where propane is affordable. Conversely, electric heaters may lead to high utility bills during peak winter months.
- Heating Speed: Propane heaters can warm spaces quickly, making them advantageous in situations where instant heat is desirable. Electric heaters tend to take longer to reach the desired temperature.
- Installation Requirements: Installing propane heaters requires a ventilation system and safe gas connections. Electric heaters come with fewer installation barriers, often needing only a standard power outlet.
± Despite these differences, both types have their own set of advantages. For instance, electric heaters are less complex to operate and can be cleaner in terms of emissions if the electricity derives from renewable sources. However, propane heaters offer flexibility in remote locations without easy access to power grids.
Propane vs. Oil Heaters
This comparison dives deeper into another key rivalry in heating solutions. When examining propane versus oil heaters, the following points emerge:
- Cost of Fuel: The price of propane and heating oil fluctuates and can influence overall heating costs. Propane tends to be less expensive at times but may also be impacted by market conditions.
- Efficiency Ratings: Propane heaters generally achieve higher efficiency ratings compared to oil, converting a greater percentage of energy into heat. This translates into savings for farmers looking to maximize their budgets.
- Environmental Impact: Both energy sources emit some greenhouse gases; however, propane burns cleaner than oil, potentially making it a more environmentally friendly choice.
- Maintenance Needs: Oil heaters typically require more maintenance to keep them running efficiently. They may need routine cleaning due to soot buildup, unlike propane heaters, which have fewer complications.
"Choosing the right heating source can significantly affect your agricultural productivity and bottom line. Taking the time to weigh options is key to making the best choice."
Each of these comparisons aids in navigating the complex landscape of heating solutions available to agricultural professionals. In essence, a thorough understanding of the differences between propane, electric, and oil heaters equips farmers with the knowledge necessary to optimize both their heating efficiency and costs.
Environmental Impact
Understanding the environmental impact of propane vented heaters is crucial for farmers and horticultural enthusiasts seeking efficient yet eco-friendly heating solutions. As the world grapples with climate change and sustainability challenges, the agricultural sector is under increasing pressure to adopt practices that minimize environmental harm. Propane vented heaters can play a significant role in this transition by offering an effective heating source while also reducing carbon footprints when managed properly.
Emissions Analysis
Emissions from heating systems, including propane vented heaters, are a key concern. While propane burns cleaner than other fossil fuels, it is not entirely free from emissions. The combustion of propane produces carbon dioxide, water vapor, and trace amounts of nitrogen oxides. For every gallon of propane used, approximately 12.7 pounds of carbon dioxide are emitted. While this figure may seem alarming, it is essential to compare it with the emissions from oil or electric systems, which are often higher.
The specific emissions to be accounted for are:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Dominant greenhouse gas contributing to climate change.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Can lead to air quality deterioration and health risks.
To evaluate emissions responsibly, a holistic view is necessary. Propane's efficiency translates to fewer emissions overall, especially when contrasted with systems that operate on oil or coal. Also, when heated spaces require less energy, this reduction supports a cleaner atmosphere.
A practical step in reducing emissions is the use of high-efficiency appliances. Models that integrate advanced burner technology can greatly lower emissions without compromising heat output. Additionally, proper maintenance, like regular checks on venting systems, ensures complete combustion and minimizes escape pollutants.
"Farmers have a unique opportunity to adopt cleaner heating practices, enhancing not just their crops but also their environmental stewardship."
Sustainable Practices in Heating
To further mitigate the environmental footprint of heating systems, implementing sustainable practices is vital. Here are some noteworthy strategies:
- Regular Maintenance: Keeping heaters well-serviced promotes optimal functioning, reducing unnecessary emissions.
- Efficient Insulation: Proper insulation of heated spaces not only keeps warmth in but also lessens the amount of fuel consumed.
- Strategic Usage: Utilizing heaters during specific times, such as when external temperatures drop significantly, can help conserve energy.
- Renewable Energy Solutions: Combining propane systems with solar or wind energy can minimize public utility reliance and lessen carbon output.
Being mindful of how propane vented heaters are used and integrating energy conservation methods can lead to sustainable farming practices. These adjustments not only preserve resources but also align with the ethics of respecting the environment.
Finalzation and proactive engagement in sustainable practices benefit not only the agricultural community but also the planet, fostering a healthier ecosystem for future generations.
Closure
In summarizing the significant insights of propane vented heaters, it becomes clear that this topic holds great relevance for those involved in agriculture and horticulture. Understanding how these heating systems operate, along with the benefits and drawbacks associated with their use, can empower farmers and agricultural enthusiasts to make informed choices tailored to their unique requirements.
Summary of Key Points
- Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness: Propane vented heaters provide a more economical option for supplying heat, especially in larger agricultural spaces where maintaining temperature is crucial. They often have lower operating costs compared to electric or oil heaters, depending on local energy prices.
- Versatility in Applications: From heating greenhouses to providing warmth for livestock, propane vented heaters demonstrate remarkable adaptability, catering to a variety of agricultural needs.
- Safety Concerns: The importance of proper installation and regular maintenance cannot be overstated. Farmers must prioritize safety measures, such as ensuring adequate ventilation to avoid gas buildup and recognizing signs of a gas leak.
- Environmental Impact Considerations: While propane is a clean-burning fuel, it’s essential to consider the broader environmental footprint of heating practices. Sustainable practices in heating can help in minimizing adverse effects on the ecosystem.
Final Thoughts on Propane Vented Heaters
Propane vented heaters present a practical solution for effective heating requirements in agricultural settings. Their efficiency, versatility, and relative cost-effectiveness make them a favorable choice for many farmers. However, responsibility comes with the benefits — ensuring that safety protocols are followed diligently and that sustainable practices are integrated into the heating process is crucial. As the agricultural landscape evolves, adapting to these heating solutions can contribute significantly to enhanced productivity and operational efficiency. For anyone involved in agriculture, staying informed about advancements and best practices in heating technology is essential for making sound decisions.
"Investing in proper heating solutions is not just about immediate comfort; it’s about protecting your crops, livestock, and ultimately your livelihood."
For further reading on best practices and safety measures in using propane vented heaters, you might find the following resources valuable:
By understanding the core elements of propane vented heaters, farmers and enthusiasts can elevate their skills and ensure a brighter, warmer future in agriculture.















