Exploring Pillar G's Role as an Intrinsic Fungicide

Intro
Agriculture faces numerous challenges, chiefly among them pest control and crop diseases. In this context, understanding the function and application of fungicides is crucial for sustainable farming practices. One such fungicide that has gained traction is Pillar G. Not all fungicides are created equal, and Pillar G stands apart due to its intrinsic properties that aid healthy plant growth. This article explores its multifaceted role in agriculture, shedding light on the mechanisms of action, practical applications, and implications for sustainable farming through a detailed framework.
Key Concepts and Terminology
Basic Definitions
Pillar G is an intrinsic fungicide, meaning it acts from within the plant rather than being applied externally. This characteristic allows it to fight pathogens effectively through systemic action. When we talk about intrinsic fungicides, we highlight those that plants absorb and distribute within their tissues, providing a resilient line of defense against fungal infections. Understanding this lays the foundation for grasping Pillar G’s potential significance in modern agriculture.
Historical Context
Historically, the battle against plant diseases has seen the use of various fungicides, evolving from inorganic compounds to more synthetic formulations. Pillar G represents a modern approach that has emerged in recent years. As farming practices shifted towards sustainability, there arose a demand for fungicides that not only control pathogens but also minimize environmental impact. Enter Pillar G—designed with the intention of integrating seamlessly within plants, making it a product of both necessity and innovation in the agricultural arsenal.
Recent Innovations and Trends
Technological Advancements
Recent advancements in agricultural science are notable, especially concerning fungicidal technology. Pillar G exemplifies the latest in this evolution. With new formulations and delivery systems, the efficiency of these fungicides has improved significantly. Scientific breakthroughs allow for better absorption characteristics, enabling crops to utilize fungicides more effectively while reducing the need for more frequent applications. This offers both cost savings and improved crop yields.
Sustainable Practices
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, Pillar G aligns with emerging agricultural practices that prioritize environmental stewardship. As farmers seek to reduce their chemical footprints, the efficiency of intrinsic fungicides becomes vital. They offer a case in point regarding how modern farming can be both productive and eco-aware. This is not just window dressing; seriously considering how products like Pillar G contribute to a healthier ecosystem is the future of agriculture.
Practical Applications and Techniques
Step-by-step Guides
For farmers looking to integrate Pillar G into their crop management strategies, understanding its application is essential:
- Pre-Application Assessment: Analyze soil and plant health, identifying specific fungal threats.
- Preparation: Make sure to mix Pillar G according to the manufacturer’s instructions, paying attention to concentration.
- Application: Utilize either foliar spray or soil injection, depending on the method specified. Accuracy counts.
- Monitoring: After application, keep tabs on plant response and any signs of residual fungal infection.
Case Studies
Consider the case of a soybean farm in Illinois, which faced severe challenges due to Fusarium wilt. After implementing Pillar G, the farmer noticed a marked reduction in disease incidence. Crop yields improved significantly, demonstrating the fungicide's effectiveness in a real-world scenario. This success story highlights how intrinsic fungicides can reshape crop health outcomes, affirming their role in contemporary agriculture.
"Utilizing Pillar G not only protects plants but contributes to a holistic farming approach by prioritizing plant health as the foremost priority."
Expanding on these principles, a growing number of agricultural practitioners are adopting Pillar G in diverse crop landscapes. As they share their experiences and outcomes, the narrative around intrinsic fungicides like Pillar G continues to strengthen.
In summary, understanding Pillar G as an intrinsic fungicide reveals its promising role in fostering sustainable agricultural practices while addressing critical challenges in the field. The balance between productivity and ecological impacts remains a central theme, guiding the future of agricultural management. Dive deeper into this evolving narrative as we explore more about the science behind it and its potential applications.
Prelims to Intrinsic Fungicides
The topic of intrinsic fungicides in agriculture is gaining momentum as stakeholders increasingly acknowledge the pivotal role these agents play in managing plant diseases. Pillar G, with its unique modus operandi, stands out amongst its peers, providing a robust mechanism for crop protection while also aligning with sustainable farming practices. The significance of understanding these compounds extends beyond mere application; they embody innovative approaches essential for future agricultural viability.
Definition and Importance
Intrinsic fungicides are naturally occurring compounds that plants synthesize to defend against fungal infections. Unlike their synthetic counterparts—often laden with harmful residues and resistance risks—intrinsic fungicides present a more holistic alternative. Essentially, they bolster a plant's immune response, enhancing resilience against diverse pathogens. When we consider the broad spectrum of threats faced by crops, from blight to mildew, intrinsic fungicides become indispensable tools, promising not only effective disease management but also reduced reliance on chemical interventions that can harm the environment and human health.
The importance of intrinsic fungicides cannot be overstated; they are vital in fostering sustainable agricultural practices. As farmers grapple with the consequences of climate change and the pressing demand for food security, these agents offer a means to protect yields while minimizing ecological footprint—a win-win scenario.
Historical Context
The journey of fungicides in agriculture has its roots embedded deep in crop protection history. Initially, farmers relied on traditional methods, such as crop rotation and cultural practices, to mitigate the damage caused by pathogens. However, the rapid evolution of agriculture, particularly post-World War II, ushered in the synthetic fungicide era. These products dominated the market, touted for their effectiveness but often criticized for their environmental toll and the biological resistance they encouraged.
In the 1980s and 1990s, as scientific understanding advanced, the concept of intrinsic fungicides began to gain traction. Agricultural scientists recognized the limitations of synthetic chemicals—often making fungi resistant and undermining soil health. Research began to pivot towards natural alternatives, revealing that many plants possess innate abilities to combat disease. This shift spurred interest in intrinsic fungicides, paving the way for innovations like Pillar G.
The historical narrative underscores a crucial evolution in agricultural philosophy; a shift toward more responsible, environmentally-friendly practices. Today, as farmers seek resilient solutions to handle an array of plant diseases, the study and implementation of intrinsic fungicides like Pillar G represents an important chapter in agricultural progress.


Pillar G: A Comprehensive Overview
Pillar G has gained attention as an intrinsic fungicide in agricultural practices. This section provides a thorough examination of its significance, exploring its chemical makeup, how it functions, and the various ways it can be utilized in farming. Understanding these elements is vital for farmers and agricultural professionals aiming to enhance crop yields while managing fungal diseases effectively.
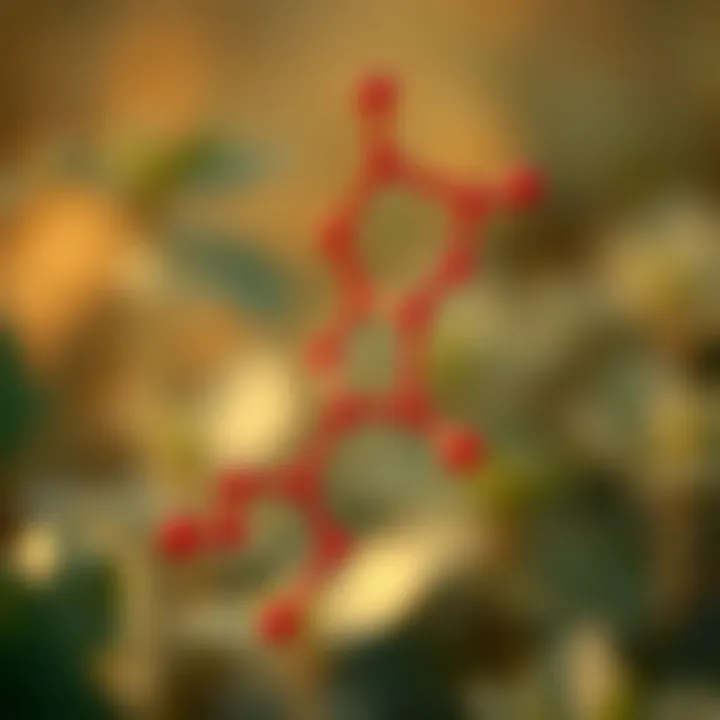
Chemical Composition
Pillar G contains a complex mix of active ingredients, prominently showcasing its effectiveness. The core component often includes compounds like Boscalid and other formulations tailored for different crops.
- Boscalid is known for its mode of action against a broad spectrum of fungal pathogens, particularly targeting diseases such as Botrytis cinerea, which plagues a variety of crops including grapes and strawberries.
- The formulation may also be blended with other fungicidal agents to create a cocktail that maximizes effectiveness, thus ensuring a multifaceted approach to disease management.
Additionally, understanding the chemical needs for specific crop types can lead to better application strategies. This knowledge allows farmers to choose the right concentrations and adjust their application schedules to best suit their crop cycles.
Mechanism of Action
The relevance of Pillar G lies in its unique mechanism, setting it apart from other fungicides. Unlike many options in the market, it works not just by inhibiting fungal growth but also by preventing the pathogens from taking root in the first place.
- Inhibition of Spore Germination: Pillar G disrupts the process of spore germination, which is critical for controlling infection onset. This means that even before a farmer notices any signs of disease, Pillar G works quietly in the background to keep potential threats at bay.
- Cellular Disruption: At a cellular level, the ingredients in Pillar G target critical pathways in fungal cells, causing dysfunctional growth and ultimately leading to their death. This characteristic speaks to its efficacy and the reduced likelihood of resistance development over time.
"Understanding how Pillar G operates allows us to not only optimize its use but also enhances our entire crop management strategy."
Forms of Application
Recognizing the various forms in which Pillar G can be applied is essential for maximizing its potential benefits. This fungicide is available in several application forms suitable for different farming practices.
- Liquid Formulations: These can be easily mixed with water for foliar sprays. Liquid applications are often preferred for their ability to cover large surface areas and penetrate dense canopies.
- Granular Formulations: Granules may be attached to the soil and slowly dissolve, providing a sustained release of the fungicide. This method is particularly advantageous for certain soil-borne diseases, ensuring that the protective action lingers throughout the growing season.
- Seed Treatments: Using Pillar G as a seed treatment can offer preventative measures right from the start, protecting emerging seedlings from root diseases.
The choice of application form can significantly impact the effectiveness of Pillar G, which is why farmers must select the method that best fits their specific agricultural context.
Agricultural Applications of Pillar G
Pillar G plays a significant role in contemporary agriculture due to its intrinsic properties as a fungicide. Farmers and agricultural professionals increasingly recognize the necessity of effective crop protection solutions that not only combat pathogens but also align with sustainable practices. Understanding how Pillar G can be effectively utilized in various applications helps in maximizing its benefits while addressing the looming threats posed by fungal diseases.
Crop Protection Strategies
The use of Pillar G as an intrinsic fungicide offers farmers a robust strategy for protecting their crops against common fungal pathogens. The effectiveness of this compound must be underscored in the context of specific crops and situations.
- Targeted Efficacy: Pillar G exhibits a strong affinity for certain pathogens frequently encountered in cereals, fruits, and vegetables. Employing it strategically protects crops without harming beneficial organisms in the ecosystem.
- Application Timing: Knowledge about the timing of application can greatly enhance the efficacy of Pillar G. Early intervention, especially at the onset of disease outbreaks, minimizes crop loss. Monitoring field conditions and environmental factors ensures that farmers can apply Pillar G at the most impactful moments.
- Rotation with Other Fungicides: Integrating Pillar G into a rotation strategy with other fungicides can also reduce the risk of resistance development among pathogens. This not only prolongs the lifespan of various fungicide classes but also keeps crops consistently protected, allowing for higher yields.
“Using Pillar G effectively means understanding your crop’s vulnerabilities and monitoring disease patterns closely.”
Integration with Sustainable Farming
The path toward sustainability in agriculture necessitates a careful evaluation of the inputs used in farming practices. Pillar G fits this narrative well due to its compatibility with integrated pest management approaches and organic farming principles.
- Biodegradability: One of the unique selling points of Pillar G is its environmentally friendly profile. Unlike some conventional fungicides, which may share a long-term legacy in the soil, Pillar G degrades more rapidly, making it a suitable choice for farmers keen on eco-friendly practices.
- Minimal Residual Impact: When considering the broader ecosystem, it is crucial to implement solutions that do not adversely affect soil health or water bodies. Pillar G's reduced residual impact means that it can be part of a broader sustainable farming strategy that protects water quality and pest biodiversity.
- Compatibility with Organic Practices: Farmers exploring organic certification options may find that the characteristics of Pillar G allow it to be integrated into their practices more seamlessly than traditional, harsher chemicals. It supports organic management without sacrificing crop health.
In summary, the agricultural applications of Pillar G provide both a shield against pathogens and contribute to sustainable farming systems. Understanding these applications forms a crucial part of maximizing its potential in modern agriculture.
Benefits of Using Pillar G
Pillar G stands out in the realm of agriculture not just as another tool in the toolbox but as a key player in effective crop disease management. The benefits of this intrinsic fungicide extend beyond mere pathogen control, influencing both farming practices and economic outcomes. Understanding these benefits can empower farmers and agricultural enthusiasts alike to make informed decisions that align with sustainable farming principles.
Efficacy Against Common Pathogens
One of the standout features of Pillar G is its remarkable efficacy against a variety of common pathogens. Whether it's the relentless Fusarium species or the notorious Powdery Mildew, Pillar G shows a strong performance in keeping these threats at bay.
- Broad Spectrum: The chemical composition allows it to combat multiple pathogens simultaneously, alleviating the need for using several different products. This spectrum helps minimize the frequency of applications, making it a time-saver in the field.
- Faster Action: Farmers often observe results in a much shorter timeframe compared to traditional fungicides. This rapid response can significantly enhance the health of plants, reducing the impact of diseases rapidly.
- Field Trials Supporting Efficacy: Numerous studies conducted in real farming environments back up these claims. For instance, trials have recorded an average reduction of disease incidence by over 50% in crops treated with Pillar G.
"The ability of Pillar G to target key pathogens without compromising plant health is a game-changer for sustainable farming practices."
— Crop Protection Study 2022


Reduced Resistance Development
Another critical benefit of Pillar G is its role in the lower risk of resistance development among pathogens. As the agricultural community grapples with the increasing issue of fungicide resistance, Pillar G presents a viable solution.
- Unique Mode of Action: Unlike many fungicides that function by inhibiting a single mechanism in pathogens, Pillar G operates via multiple pathways. This multi-faceted approach makes it harder for pathogens to adapt and develop resistance.
- Extended Longevity: The strategic deployment of Pillar G in crop management can lead to decreased reliance on traditional fungicides that often contribute to resistance development. This prolongs the efficacy of all fungicides used in tandem and maintains their effectiveness over time.
- Promoting Diverse Management Strategies: By incorporating Pillar G into a broader integrated pest management (IPM) strategy, farmers can create a synergistic approach. This entails rotating fungicide classes and diversifying application methods, resulting in a healthier crop ecosystem.
In summary, the benefits of using Pillar G transcend simple fungicidal action. With its proven effectiveness against common diseases and its role in delaying resistance, it offers a practical and strategic advantage for farmers committed to enhancing their agricultural practices. As always, proper application techniques and adherence to guidelines are crucial to harnessing the full potential of any fungicide, including Pillar G.
Limitations and Concerns
Understanding the limitations and concerns surrounding Pillar G as an intrinsic fungicide is crucial for farmers and agricultural stakeholders. While this compound offers significant benefits, being informed about its potential drawbacks helps ensure responsible and effective usage in agricultural practices. In this section, we shall explore two primary aspects: the potential side effects and the environmental impact associated with Pillar G.
Potential Side Effects
Pillar G, like any fungicide, can have side effects that farmers need to take into consideration. Here are some of the potential side effects:
- Plant Sensitivity: Certain crops might exhibit sensitivity to Pillar G, leading to unexpected phytotoxic reactions. For example, while it works wonders on tomatoes, it could potentially harm plants like peas if not applied correctly.
- Soil Health: Some studies suggest that intrinsic fungicides may alter beneficial microbial populations in the soil. This change can disrupt vital functions such as nutrient cycling, critical for crop growth.
- Resistance Development: Usage of any antifungal agent can lead to resistance over time. While Pillar G shows reduced resistance development compared to conventional fungicides, there's still a risk if used excessively or improperly.
"Being aware of potential side effects enables farmers to adopt better practices, ensuring Pillar G's efficacy while safeguarding plant health."
Payers of good quality agriculture should always monitor crops for adverse reactions when using Pillar G, adjusting application rates and timing as needed. This level of scrutiny can help minimize risks and facilitate steady, healthy crop yields.
Environmental Impact
The environmental implications of using Pillar G merit careful review as well. Here are a few key points to consider:
- Water Contamination: One concern with using fungicides is the potential for runoff into water bodies. If not managed properly, excess use of Pillar G could contaminate nearby lakes or rivers, affecting aquatic ecosystems.
- Non-target Organisms: There is a risk that beneficial insects or pollinators could be adversely affected by the application of Pillar G in agricultural fields. This can have a cascading effect on biodiversity and ecosystem health.
- Long-term Soil Effects: Some research indicates that frequent use of fungicides could lead to diminished soil quality over time, influencing its fertility and structure. Maintaining a balance in utilizing Pillar G, along with other practices like crop rotation and organic amendments, can prove beneficial.
In summary, while Pillar G offers tangible advantages in agricultural fungicide usage, awareness of its limitations and potential concerns must be at the forefront of any farming strategy. Understanding both sides of the coin allows for better decision-making and sustainable practices that can greatly enhance crop health while protecting the environment.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding fungicides like Pillar G is fundamental to their acceptance and implementation in agricultural practices. This framework ensures that products are thoroughly evaluated for safety and efficacy before they enter the market. Not only does it protect the health of consumers and the environment, but it also shapes agricultural practices by setting standards that must be adhered to. Understanding these regulations is crucial for farmers and agricultural stakeholders aiming to use Pillar G responsibly and effectively.
Global Regulations on Fungicides
Globally, fungicides are governed by a multitude of regulations, varying significantly from one region to another. Regulatory bodies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and the European Commission in the EU, play pivotal roles. These agencies conduct rigorous assessments, factoring in the potential impacts on human health, non-target organisms, and overall ecosystem health.
"Regulations ensure that no stone is left unturned when evaluating a fungicide's impact, safeguarding our food supply and environment."
- Efficacy studies and data: Companies are required to provide substantial evidence showcasing the effectiveness of Pillar G against various pathogens.
- Toxicology assessments: Evaluations to ensure that the product does not pose significant health risks to farm workers or consumers.
- Residue guidelines: Setting limits on how much residual product can remain on crops at the time of harvest, ensuring food safety.
Multiple nations also come together under global treaties, collectively acknowledging the necessity of control measures, such as The Rotterdam Convention that aims to promote shared responsibility in the handling of hazardous chemicals. This ensures that Pillar G's use aligns with international safety standards.
Region-Specific Guidelines
Diving deeper into regional specifics, guidelines can reflect local agricultural needs, pest pressures, and even climatic conditions. Countries often tailor regulations to address unique local challenges.
For instance:
- United States: Here, the EPA regulates each fungicide's registration through processes that demand rigorous data submission and field trial outcomes. This ensures that the unique agricultural landscape of the U.S. is taken into account.
- European Union: The EU typically adopts a precautionary principle, demanding extensive environmental impact assessments before issuing regulations. Pillar G’s deployment in European markets might come with tighter controls regarding its application times and maximum dosages than in other regions.
- Brazil: As one of the largest agricultural producers, Brazil has a regulatory structure that not only allows for quicker registration processes but also considers local agronomic conditions and pest pressures.
Farmers should stay abreast of the evolving regulations in their respective regions by checking resources such as FDA and USDA websites or local agricultural departments . To remain compliant, engaging in continuous education programs about these regulations is beneficial. Having this knowledge not only ensures proper application but also fosters sustainable farming practices while protecting public health and environmental integrity.
Future Directions in Fungicide Research
In recent years, the agricultural sector has experienced a surge in the demand for effective, sustainable solutions to manage crop diseases. The advent of Pillar G as an intrinsic fungicide is a prime example of this trend. As research progresses, the future directions in fungicide research are pivotal not only for enhancing agricultural productivity but also for aligning with eco-friendly practices. Current formulations may serve their purpose, but the drive for innovation must continue unabated.
Innovation in Fungicidal Formulations


The landscape of fungicides is constantly evolving, with emphasis on creating products that boast higher efficacy and lower environmental impact. Innovation in fungicidal formulations encompasses developments like advanced delivery systems, which enhance the longevity and effectiveness of active ingredients.
For instance, recent advancements in nanoparticle technology promise to improve the absorption of fungicides into plant tissues, boosting their disease-fighting capabilities. Traditional formulations often struggle against resistant strains of pathogens, making this innovation vital. These new formulations also consider the timing and method of application, ensuring that farmers can optimize their resources more efficiently.
In addition to nanoparticle technology, we're beginning to see more emphasis on bio-based fungicides. These products utilize naturally occurring substances or microbial organisms to combat pathogens, serving not only as viable alternatives but also reducing chemical load in agricultural practices. Such shifts align with growing consumer preferences for organically produced food.
- Key Areas of Focus:
- Enhancing absorption through innovative delivery systems
- Developing bio-based alternatives
- Improving application techniques for better resource management
Biotechnological Advances
Biotechnological advances represent the cornerstone of future research directions in the fungicide domain. With an increasing need to mitigate crop losses and manage diseases, biotechnology offers solutions that are both responsive and resilient. Gene editing techniques, such as CRISPR, can be harnessed not only for developing disease-resistant crops but also for creating more targeted fungicides.
For example, research in plant genomics has opened doors to understanding the specific molecular mechanisms that pathogens use to infiltrate plants. With such knowledge, scientists can formulate fungicides that interrupt these processes, thereby minimizing crop damage and dependency on broad-spectrum solutions. This targeted approach lessens the likelihood of developing fungicide-resistant strains, which has long been a concern in the agricultural community.
Moreover, the integration of precision agriculture technology can further refine fungicide application methods. Sensors and data analytics can guide farmers in applying fungicides at optimal times and dosages, significantly improving their effectiveness while reducing waste.
- Benefits of Biotechnological Advances:
- Development of pathogen-specific fungicides
- Enhanced resistance to fungicide resistance through targeted applications
- Improved data-driven decision-making in fungicide application
"Understanding and embracing these innovations is essential for farmers looking to secure their outputs and sustainability in an ever-changing climate."
In summary, the pathway forward in fungicide research is illuminated by new formulations and groundbreaking biotechnological innovations. As the agricultural industry adapts to challenges, it is crucial that stakeholders stay informed and ready to integrate these advancements into their practices.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Pillar G
The exploration of case studies demonstrating the successful implementation of Pillar G is essential in grasping its practical applications and effectiveness as an intrinsic fungicide. Understanding how Pillar G has fared in real-world scenarios allows farmers and agricultural stakeholders to glean insights that can directly influence their strategies and outcomes.
Field Trials Overview
Field trials are the backbone of agricultural research, providing evidence that informs best practices and product usage. With Pillar G, several field trials have been conducted across diverse crop types and environments. These trials yielded significant findings concerning Plant Health, overall yield improvement, and pest resistance development.
- Diverse Crop Testing: Across various crops—such as tomatoes, grapes, and wheat—Pillar G has shown a robust efficacy against common fungal pathogens. In one trial conducted in California, researchers found that crops treated with Pillar G had a 30% reduction in fungal infection rates compared to untreated control groups.
- Integrating with Environmental Conditions: An interesting finding from a trial in the Pacific Northwest demonstrated that the efficacy of Pillar G improved with specific climatic conditions. For instance, the product performed exceptionally well in cooler temperatures, showcasing its adaptability to varying environmental factors.
"Field trials not only validate efficacy but also help to refine application methods, adjusting for real-world conditions that farmers encounter."
Comparative Analysis with Other Fungicides
Competitively, it is important to assess where Pillar G stands against conventional fungicides like chlorothalonil and tebuconazole. Case studies provide that clarity. While Pillar G excels in certain aspects, it is crucial to align its properties with the needs of specific agricultural practices.
- Efficacy Rates: In head-to-head comparisons, Pillar G has demonstrated lower levels of pathogen resistance development than its counterparts. For instance, a study revealed that ongoing treatments with chlorothalonil led to a higher rate of resistance in fungal populations, affecting long-term effectiveness.
- Safety and Environmental Concerns: Case studies emphasize that Pillar G poses fewer risks to non-target organisms compared to traditional fungicides. This becomes especially relevant for organic farming practices, where additional considerations regarding pesticide residues are paramount.
This comparative perspective not only sheds light on the strengths of Pillar G but also encourages further research in enhancing its formulations. As insights from these case studies emerge, they pave the way for refining agricultural practices, making it easier for farmers to navigate the complexities of pest management.
Ending and Recommendations
In summing up the journey through the various facets of Pillar G as an intrinsic fungicide, it's paramount to reflect on a few key points. Understanding this compound not only as a protective measure against pathogens but also as a player in sustainable agricultural practices raises its profile significantly. The agricultural community stands at a critical junction where the judicious application of fungicides can make or break crop yield and quality. Recognizing Pillar G's potential thereby becomes essential in the contemporary farming narrative.
Summary of Findings
Throughout this exploration, several salient findings regarding Pillar G have been highlighted:
- Mechanisms of Action: Pillar G’s unique mode of action targets specific fungi, inhibiting their growth effectively. This provides an edge over traditional fungicides that might have broader but less targeted effects.
- Agricultural Applications: Whether through foliar sprays or soil treatments, Pillar G demonstrates versatility in application, catering to various crop needs.
- Efficacy and Sustainability: The integration of Pillar G into current farming practices can reduce dependency on more harmful chemicals, aligning with a sustainable approach that today's farmers are increasingly seeking.
Moreover, the reduced potential for resistance development—itself a serious concern in modern agriculture—reinforces its importance in the arsenals of farmers striving for long-term success.
"By carefully considering the integration of Pillar G and aligning its use with best practices, we not only enhance our crop health but also foster a more sustainable farming ecosystem."
Best Practices for Use
To harness the full potential of Pillar G, here are some strategic recommendations:
- Monitoring and Assessment: Regularly evaluate crop health and pathogen presence to determine the optimal timing for Pillar G application. Understanding local conditions and specific crop needs plays a crucial role in effectiveness.
- Integrate with Other Methods: Employ Pillar G as part of an integrated pest management (IPM) strategy. Combining it with biological control methods can enhance the overall fungicidal effect and reduce the chance of resistance.
- Adapt Application Techniques: Utilize the appropriate application method—whether it’s spraying or drenching—based on the crop type and the specific fungal threats being addressed.
- Stay Informed on Regulations: Keep abreast of local regulations and guidelines regarding the use of Pillar G and other fungicides, ensuring compliance and promoting safe usage.
In summary, Pillar G is more than a fungicide; it's a transformative element in agriculture when used thoughtfully. By adhering to these practices, farmers can maximize their harvests while upholding environmental stewardship, making strides towards a sustainable future.















